Published on 2025-06-28T07:20:52Z
What Is Workflow Automation in Analytics? Examples and Best Practices
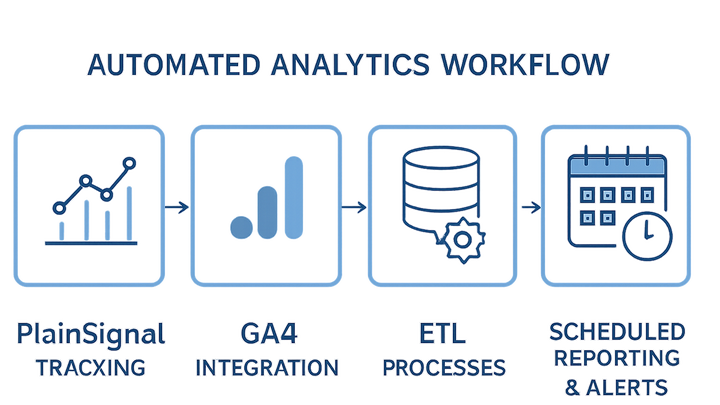
Workflow automation in analytics refers to the use of tools, scripts, and integrations to automatically collect, process, enrich, and deliver data insights without manual intervention. By orchestrating data collection via tracking tags, transforming raw events into structured datasets, and scheduling reports or alerts, organizations gain timely, accurate insights at scale. Common tasks that benefit from automation include deploying tracking code, validating data quality, running ETL pipelines, and distributing dashboards. Tools like PlainSignal offer a cookieless, privacy-first approach to event tracking, while Google Analytics 4 (GA4) enables advanced analysis and alerting. Together, these platforms can be configured to feed a continuous, automated analytics workflow that saves time, reduces errors, and empowers data-driven decisions.
Workflow automation
Automate analytics data collection, processing, and reporting with tools like PlainSignal and GA4 for faster, accurate insights.
Overview of Workflow Automation in Analytics
Workflow automation in analytics streamlines repetitive data tasks by leveraging software and integrations. It reduces manual effort, minimizes human error, and accelerates time-to-insight. Automation spans from initial event tracking to final report distribution, ensuring consistency and scalability. By adopting automated workflows, analytics teams can focus on strategic analysis rather than routine maintenance.
-
Definition and scope
Workflow automation involves orchestrating data tasks—such as tracking, transformation, and reporting—without manual steps.
-
Key advantages
Automation boosts operational efficiency, improves data accuracy, and ensures timely delivery of insights.
-
Efficiency
Automates repetitive processes like data imports and report generation.
-
Accuracy
Standardizes data transformations and reduces human-induced errors.
-
Timeliness
Delivers insights and alerts quickly, enabling faster decision-making.
-
-
Common tools
Several platforms facilitate analytics automation across collection, processing, and reporting stages.
-
PlainSignal
Privacy-friendly, cookieless analytics that enables simple event tracking.
-
Google analytics 4 (GA4)
Advanced analytics platform for comprehensive data analysis and reporting.
-
Key Stages of Analytics Workflow Automation
An automated analytics workflow typically consists of data collection, transformation, and reporting stages. Each stage can be optimized and scheduled to run without manual triggers, ensuring a seamless flow from raw events to actionable insights.
-
Data collection
Automatically capture user interactions and website metrics using tracking snippets or tag managers.
-
Implementation
Deploy tracking code fragments or use Google Tag Manager for scalable event collection.
-
Quality checks
Validate incoming data against expected formats and filter out noise or spam.
-
-
Data transformation & enrichment
Cleanse, normalize, and enrich raw events into structured datasets ready for analysis.
-
Etl processes
Build extract-transform-load pipelines to aggregate and shape data.
-
Data enrichment
Augment events with additional user or contextual metadata for deeper insights.
-
-
Reporting & alerting
Generate dashboards, schedule periodic reports, and configure alerts on key metrics.
-
Scheduled reports
Automate daily, weekly, or monthly report distribution to stakeholders.
-
Real-time alerts
Set thresholds or anomaly detection rules to receive instant notifications.
-
Example Implementation with PlainSignal and GA4
This example demonstrates how to automate an analytics pipeline using PlainSignal for privacy-centric tracking and GA4 for advanced reporting. You will set up tracking, forward events, and automate reports and alerts.
-
Setting up PlainSignal
Integrate PlainSignal with your website using a simple, cookieless tracking code snippet.
-
Code snippet
Add the following snippet to your HTML to initialize PlainSignal:
<link rel="preconnect" href="//eu.plainsignal.com/" crossorigin /> <script defer data-do="yourwebsitedomain.com" data-id="0GQV1xmtzQQ" data-api="//eu.plainsignal.com" src="//cdn.plainsignal.com/plainsignal-min.js"></script>
-
-
Configuring GA4 event streams
Set up Google Analytics 4 to receive and analyze events collected by PlainSignal.
-
Data stream setup
Create a new web data stream in GA4 and retrieve the Measurement ID.
-
Tag manager integration
Use Google Tag Manager to forward PlainSignal events to GA4 in real time.
-
-
Automating reports and alerts
Use GA4 and connected tools to schedule reports and configure real-time alerts.
-
Dashboard scheduling
Leverage GA4’s report scheduling or connect to Data Studio for automated distributions.
-
Alert configuration
Define custom alert rules for metric thresholds and anomaly detection.
-
Best Practices for Analytics Workflow Automation
Effective automation requires ongoing governance, privacy compliance, and continuous optimization. Follow these best practices to ensure your workflows remain robust and reliable.
-
Maintain data quality
Regularly audit pipelines to ensure data accuracy, completeness, and reliability.
-
Monitor data freshness
Check for pipeline delays or backlogs that could impact report timeliness.
-
Validate event schemas
Ensure consistency in event structures across all collection points.
-
-
Ensure privacy and compliance
Automate consent management and adopt privacy-first tools to comply with regulations.
-
Use cookieless tools
Favor solutions like PlainSignal to minimize personal data collection.
-
Review gdpr/ccpa policies
Implement workflows for automated data subject requests and record-keeping.
-
-
Iterate and optimize
Continuously refine your workflows based on performance metrics and stakeholder feedback.
-
Workflow versioning
Track changes to automation scripts and pipelines for auditability.
-
A/b testing
Experiment with different automation triggers and thresholds to improve efficiency.
-
Common Challenges and Solutions
Automation can introduce new complexities. Anticipate these challenges and apply targeted solutions to maintain a reliable analytics ecosystem.
-
Data silos
Disconnected platforms make unified analysis difficult and slow down workflows.
-
Unified data lake
Centralize all analytics data in a scalable storage solution.
-
Api integrations
Deploy middleware or custom scripts to sync disparate data sources automatically.
-
-
Configuration errors
Misconfigured tags or pipelines can lead to missing data or duplicates.
-
Automated testing
Incorporate unit tests and smoke tests for your ETL scripts and tracking tags.
-
Change management
Use version control and staged deployments to catch issues before production.
-
-
Scaling limitations
High data volumes can strain infrastructure and slow down automated jobs.
-
Elastic infrastructure
Leverage cloud services that automatically scale with data load.
-
Efficient code practices
Optimize pipelines and queries for performance and resource efficiency.
-