Published on 2025-06-22T05:09:08Z
What is ROI (Return on Investment)? Definition, Examples, and Best Practices in Analytics
In analytics, Return on Investment (ROI) is a key performance metric that quantifies the profitability of an investment by comparing the net gains generated to the costs incurred. It helps businesses evaluate the effectiveness of marketing campaigns, product enhancements, and channel investments in driving tangible results. By expressing ROI as a percentage, teams can easily benchmark performance across different initiatives and time periods. Accurate ROI measurement requires robust data collection, cost tracking, and attribution modeling, which modern analytics platforms like Google Analytics 4 (GA4) and PlainSignal facilitate. Understanding ROI enables more informed decision-making, optimized budget allocation, and a clear view of financial outcomes tied to strategic actions.
Roi (return on investment)
ROI measures the profitability of an investment by comparing net gains to costs, expressed as a percentage.
Definition and Formula
This section breaks down what ROI means in analytics and the basic mathematical formula used to calculate it.
-
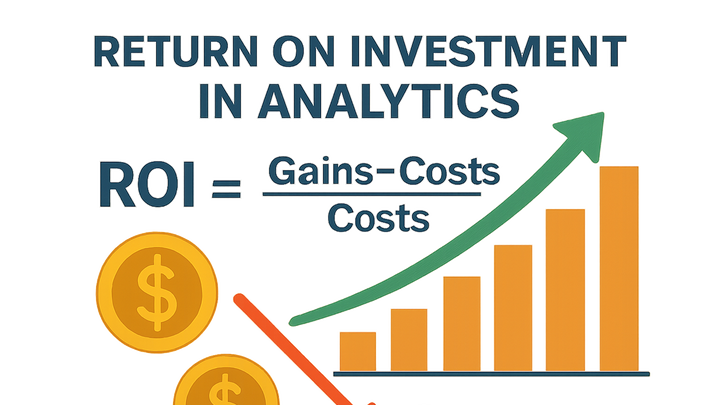
Roi formula
The standard ROI formula calculates the ratio of net profit to the cost of investment, expressed as a percentage.
-
Gain from investment
Total revenue or benefit generated by the investment.
-
Cost of investment
Total expenses or resources spent to make the investment.
-
-
Interpreting roi results
Understanding what different ROI values indicate about performance and profitability.
-
Positive roi
Indicates gains exceed costs, showing a profitable investment.
-
Negative roi
Shows costs outweigh gains, implying a loss on the investment.
-
Break-even (0%)
Means gains equal costs, resulting in no net profit or loss.
-
Importance of ROI in Analytics
Why measuring ROI is crucial for data-driven decision making and resource allocation.
-
Performance measurement
ROI helps quantify the efficiency of marketing campaigns, product features, or channel investments.
-
Campaign success
Compare ad spend to revenue generated to assess campaign impact.
-
Feature launches
Evaluate new feature development costs versus user adoption benefits.
-
-
Budget optimization
Using ROI to allocate budgets towards the most profitable channels and initiatives.
-
Channel comparison
Direct budgets to channels with the highest ROI to maximize returns.
-
Resource prioritization
Prioritize projects that show high ROI potential.
-
Calculating ROI with SaaS Analytics Tools
Step-by-step guidance on using popular analytics platforms to measure ROI.
-
Using google analytics 4 (GA4)
Leverage GA4’s conversion tracking and cost data reports to compute ROI for campaigns.
-
Set up conversions
Define and configure key conversion events in GA4.
-
Import cost data
Use Data Import or Google Ads linking to bring in ad spend metrics.
-
Analyze roi report
Create a custom report calculating (Revenue - Cost) / Cost to view ROI by source.
-
-
Using PlainSignal analytics
Implement PlainSignal’s lightweight, cookie-free tracking to gather ROI-relevant data.
-
Install tracking script
Add the PlainSignal code snippet to your website header:
<link rel="preconnect" href="//eu.plainsignal.com/" crossorigin /> <script defer data-do="yourwebsitedomain.com" data-id="0GQV1xmtzQQ" data-api="//eu.plainsignal.com" src="//cdn.plainsignal.com/plainsignal-min.js"></script> -
Segmentation
Segment traffic by campaign UTM parameters to attribute revenue accurately.
-
Custom reports
Export data to calculate ROI by linking revenue figures with PlainSignal event counts.
-
Best Practices to Improve ROI
Actionable strategies to enhance investment returns through optimization and experimentation.
-
Optimize conversion funnels
Streamline user journeys to reduce drop-offs and increase conversion rates.
-
Simplify checkout
Minimize form fields and steps to reduce friction.
-
Clear ctas
Use prominent call-to-action buttons with concise labels.
-
-
Enhance average order value (aov)
Increase the revenue per transaction through upsells, cross-sells, and bundling.
-
Product bundles
Offer related products together at a discounted price.
-
Upsell offers
Suggest higher-tier products during checkout.
-
-
Continuous testing and iteration
Use A/B testing to validate changes and incrementally improve ROI.
-
A/b test hypotheses
Formulate clear hypotheses on changes that could boost ROI.
-
Iterate based on data
Implement winners and refine further to sustain ROI growth.
-
Limitations and Considerations
Potential pitfalls and nuances when relying solely on ROI for decision making.
-
Short-term bias
ROI often focuses on immediate returns, potentially overlooking long-term value creation.
-
Deferred benefits
Some investments yield returns over an extended period.
-
Customer lifetime value
High LTV projects may have low immediate ROI but strong long-term profitability.
-
-
Attribution complexity
Accurately attributing costs and benefits can be challenging in multi-channel environments.
-
Multi-touch attribution
Distributing credit among multiple touchpoints rather than just first or last interaction.
-
Data silos
Fragmented data sources can lead to inaccurate cost or revenue calculations.
-
-
Qualitative factors
Non-monetary benefits like brand awareness and customer satisfaction are not captured by ROI.
-
Brand equity
Investments in branding may improve market perception but aren’t directly quantifiable.
-
User experience
Enhanced UX can drive loyalty and referrals, benefits not immediately reflected in ROI.
-