Published on 2025-06-22T08:20:10Z
What is Measurement Protocol? Examples for GA4 and PlainSignal
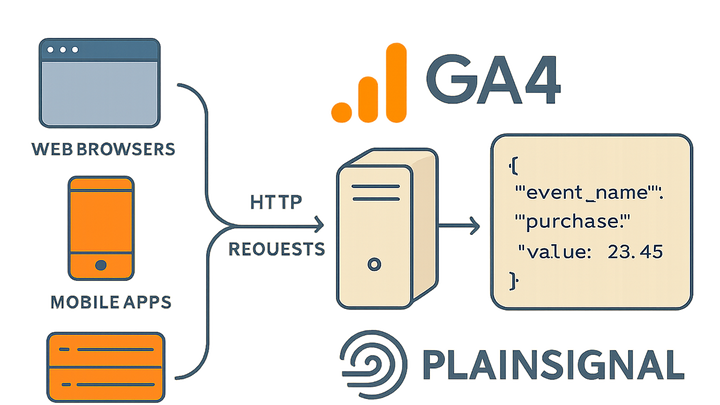
Measurement Protocol is an HTTP-based interface that allows you to send raw event data directly to analytics services, bypassing the need for client-side JavaScript.
It provides a flexible solution for server-side tracking, offline queues, and data ingestion from diverse sources like CRM systems or IoT devices.
Supported by products such as Google Analytics 4 (GA4) and cookie-free analytics platforms like PlainSignal, Measurement Protocol empowers developers and analysts to achieve comprehensive data coverage even when client-side methods are insufficient.
Events are transmitted via HTTP GET or POST requests to designated endpoints, accompanied by key-value parameters specifying details like client ID, event name, and timestamps.
This approach not only improves data accuracy and security but also aligns with privacy-first strategies by enabling cookieless tracking.
Measurement protocol
An HTTP API to send raw analytics event data directly to servers for server-side, offline, and cookieless tracking.
Definition and Importance
Explains what Measurement Protocol is and why it’s critical in the analytics ecosystem, especially for server-side and offline events.
-
Core concept
Measurement Protocol is an HTTP-based API designed to send raw interaction data to analytics platforms directly from any environment, bypassing client-side libraries.
-
Key advantages
Provides full control over data collection, enabling server-side and offline event tracking as well as customization.
-
Data continuity
Ensures events are recorded even when users are offline or in environments without JavaScript.
-
Custom parameters
Supports custom parameters for enhanced segmentation and personalized analytics.
-
Protocol Mechanics
Details the structure of Measurement Protocol requests, required parameters, authentication, and how analytics servers process incoming data.
-
Request structure
Hits are sent via HTTP GET or POST requests to specific endpoints with a payload of key-value pairs defining the event.
-
Essential parameters
Include protocol version (
v), client ID (cid), event name (en), and timestamp (qt), among others. -
Endpoint urls
GA4 uses
https://www.google-analytics.com/mp/collect?measurement_id=G-XXXX&api_secret=XXXX, while PlainSignal may usehttps://eu.plainsignal.com/mp/collect.
-
-
Authentication and identification
Mechanisms to identify users and authenticate requests, ensuring data integrity and security.
-
Client id
A unique identifier (UUID) stored in cookies or generated server-side to link user sessions.
-
Api secret (GA4)
A secret key required by GA4 Measurement Protocol to validate requests.
-
Implementation Examples
Provides concrete examples of how to implement Measurement Protocol with popular analytics services.
-
GA4 measurement protocol example
A sample cURL request sending a
purchaseevent to Google Analytics 4.-
Curl snippet
curl -X POST 'https://www.google-analytics.com/mp/collect?measurement_id=G-XXXX&api_secret=XXXX' -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d '{"client_id":"555","events":[{"name":"purchase","params":{"value":23.07}}]}'
-
-
PlainSignal tracking script
Example script tag for PlainSignal, a cookie-free analytics tool, to initiate Measurement Protocol tracking.
-
Html snippet
<link rel="preconnect" href="//eu.plainsignal.com/" crossorigin /> <script defer data-do="yourwebsitedomain.com" data-id="0GQV1xmtzQQ" data-api="//eu.plainsignal.com" src="//cdn.plainsignal.com/plainsignal-min.js"></script>
-
Use Cases and Best Practices
Explores common scenarios for using Measurement Protocol and guidelines to ensure data accuracy.
-
Common use cases
Typical applications of Measurement Protocol across various industries.
-
Server-side event tracking
Capturing backend events like order confirmations or API interactions.
-
Offline data collection
Buffering events on devices and sending them once connectivity is restored.
-
Iot and device analytics
Reporting interactions from smart devices without a browser environment.
-
-
Best practices
Recommendations to maximize the reliability and usefulness of Measurement Protocol data.
-
Validate payloads
Ensure all required parameters are present and correctly formatted to avoid data loss.
-
Handle duplicates
Implement deduplication logic to prevent counting the same event multiple times.
-
Accurate timestamps
Include precise event timestamps to maintain proper event sequencing.
-